Osteoarthritis (OA) and spondylosis (OA of the spine) can result in pain and functional impairment and account for significant morbidity burdens among U.S. civilian and military populations.1–3 Management of cases of OA requires substantial health care resources and incurs considerable costs.4 A recent MSMR analysis described the incidence of OA and spondylosis diagnoses among active component service members of the U.S. Armed Forces during 2016–2020.5 Crude annual incidence rates of both conditions decreased markedly from 2016 through 2020 with declines evident in all of the demographic and military subgroups examined.5
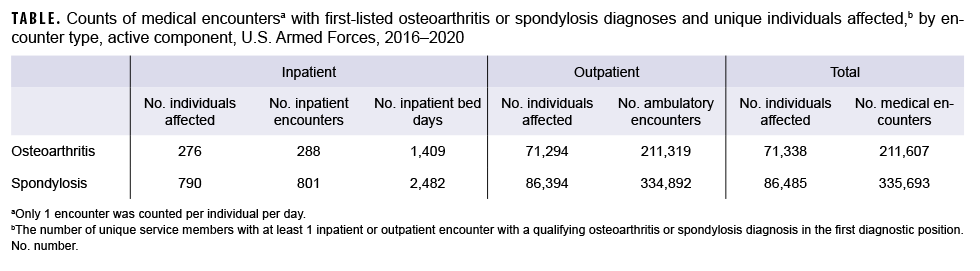
This snapshot summarizes the total numbers of inpatient and outpatient encounters with an OA or spondylosis diagnosis in the first diagnostic position and the total numbers of unique individuals affected by these conditions during the same 5-year surveillance period. Totals included both incident and prevalent cases. Among active component service members during 2016–2020, a total of 71,338 unique individuals were affected by OA (Table). These individuals contributed a total of 211,607 OA-related medical encounters, representing an average of 3 medical encounters per affected individual. The vast majority (99.9%) of the total OA-related medical encounters were in outpatient settings. Service members affected by OA who had 1 or more OA-related hospitalizations (n=276) were associated with a total of 1,409 hospital bed days.
Between 2016 and 2020, a total of 86,485 unique individuals were affected by spondylosis (Table). These individuals had a total of 335,693 spondylosis-related medical encounters, representing 4 medical encounters per affected individual. Similar to OA, the vast majority (99.8%) of the total spondylosis-related medical encounters were in outpatient settings. Spondylosis-related hospitalizations (n=790) accounted for a total of 2,482 hospital bed days.
References
1. Abramoff B, Caldera FE. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, diagnosis, and treatment options. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2):293–311.
2. Vina ER, Kwoh CK. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: Literature update. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2018;30(2):160-167.
3. Armed Forces Health Surveillance Division. Absolute and relative morbidity burdens attributable to various illnesses and injuries, active component, U.S. Armed Forces, 2020. MSMR. 2021;28(5):2–9.
4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Prevalence of doctor-diagnosed arthritis and arthritis-attributable activity limitation United States, 2010–2012. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2013;62(44):869–873.
5. Williams VF, Ying S, Stahlman S. Update: Osteoarthritis and spondylosis, active component, U.S. Armed Forces, 2016–2020. MSMR. 2021;28(12):2–13.