What are the new findings?
In 2021, as in prior years, the medical conditions associated with the most medical encounters, the largest number of affected service members, and the greatest number of hospital days were in the major categories of injuries, musculoskeletal disorders, and mental health disorders. Despite the pandemic, COVID-19 accounted for less than 2% of total medical encounters and bed days in active component service members.
What is the impact on readiness and force health protection?
Injuries, musculoskeletal disorders, and mental health disorders detract from service members’ individual readiness and deployability and hinder the ability to execute the missions of the Armed Forces. Continued focus on enhanced measures to prevent and treat such disorders is warranted.
Perceptions of the relative importance of various health conditions in military populations often determine the natures, extents, and priorities for resources applied to primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention activities. However, these perceptions are inherently subjective and may not reflect objective measures of the relationship between the conditions and their impact on health, fitness, military operational effectiveness, health care costs, and so on.
Several classification systems and morbidity measures have been developed to quantify the “public health burdens” that are attributable to various illnesses and injuries in defined populations and settings.1 Not surprisingly, different classification systems and morbidity measures lead to different rankings of illness- and injuryspecific public health burdens.2
For example, in a given population and setting, the illnesses and injuries that account for the most hospitalizations are likely different from those that account for the most outpatient medical encounters. The illnesses and injuries that account for the most medical encounters overall may differ from those that affect the most individuals, have the most debilitating or longlasting effects, and so on.2 Thus, in a given population and setting, the classification system or measure used to quantify condition-specific morbidity burdens shapes to a large extent the conclusions that may be drawn regarding the relative importance of various conditions and, in turn, the resources that may be indicated to prevent or minimize their impacts.
This annual summary uses a standard disease classification system (modified for use among U.S. military members) and several health care burden measures to quantify the impacts of various illnesses and injuries among members of the active component of the U.S. Armed Forces in 2021.
Methods
The surveillance period was 1 January through 31 December 2021. The surveillance population included all individuals who served in the active component of the U.S. Army, Navy, Air Force, or Marine Corps at any time during the surveillance period. All data used in this analysis were derived from records routinely maintained in the Defense Medical Surveillance System (DMSS). These records document both ambulatory encounters and hospitalizations of active component members of the U.S. Armed Forces in fixed military and civilian (if reimbursed through the Military Health System [MHS]) treatment facilities worldwide.
For this analysis, DMSS data for all inpatient and outpatient medical encounters of all active component members during 2021 were summarized according to the primary (first-listed) diagnosis (if reported with an International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision [ICD-10] code between A00 and T88; U07.0, U07.1 or U09.9; an ICD-10 code beginning with Z37; or Department of Defense [DoD] unique personal history codes DOD0101–DOD0105). For summary purposes, all illness- and injury-specific diagnoses (as defined by the ICD-10) were grouped into 153 burden of disease-related “conditions” and 25 “categories” based on a modified version of the classification system developed for the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) Study.1 The most recently added conditions include COVID-19 and polycystic ovarian syndrome, both of which were added in the 2020 burden analysis. The 2019 MSMR analyses grouped illness-and injury-specific diagnoses into 151 conditions, which was an increase over the prior 142 conditions used in previous MSMR analyses. The increase to 151 conditions in the 2019 analysis was informed by the review of preliminary results of the 2019 burden analysis which revealed that within 8 of the 22 “all other” conditions, large numbers of medical encounters were attributable to 9 diagnosis codes or groups of codes (cervicalgia, chronic pain, vaginitis and vulvitis, urinary tract infection and cystitis, deviated nasal septum, tinea skin infections, constipation, testicular hypofunction, and gout). Based on this finding, these diagnosis codes or groups of codes were broken out and treated as separate burden of disease-related conditions in the analysis.
In general, the GBD system groups diagnoses with common pathophysiologic or etiologic bases and/or significant international health policymaking importance. In this analysis, some diagnoses that are grouped into single categories in the GBD system (e.g., mental health disorders) were disaggregated to increase the military relevance of the results. Also, injuries were classified by affected anatomic site rather than by cause because external causes of injuries are incompletely reported in military outpatient records.
The “morbidity burdens” attributable to various “conditions” were estimated based on the total number of medical encounters attributable to each condition (i.e., total hospitalizations and ambulatory visits for the condition with a limit of 1 encounter per individual per condition per day), numbers of service members affected by each condition (i.e., individuals with at least 1 medical encounter for the condition during the year), and total bed days during hospitalizations for each condition.
Results
Morbidity burden, by category
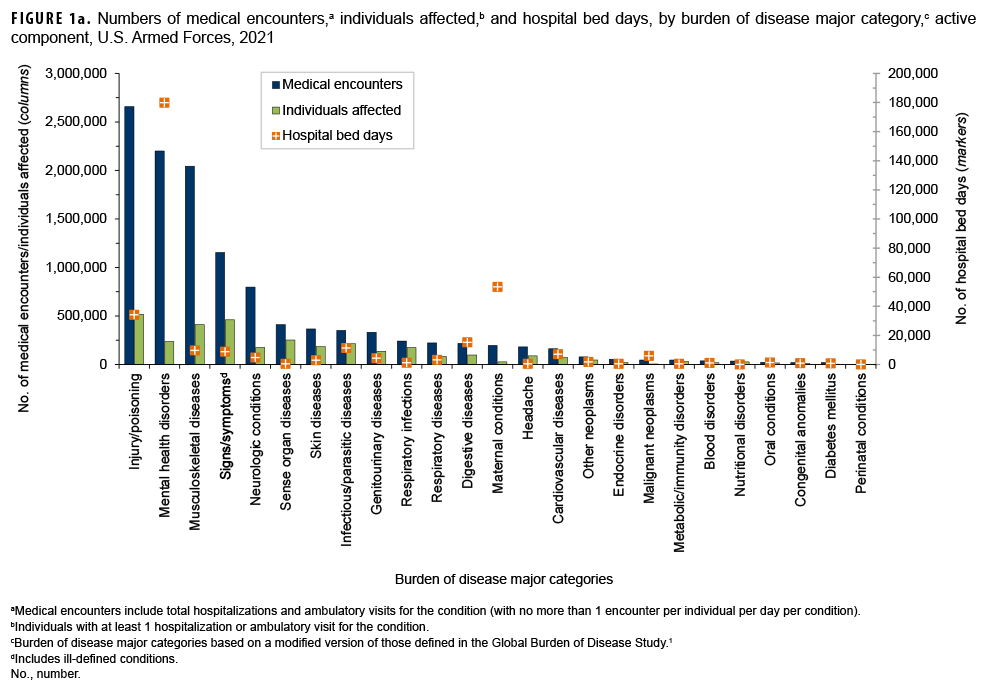
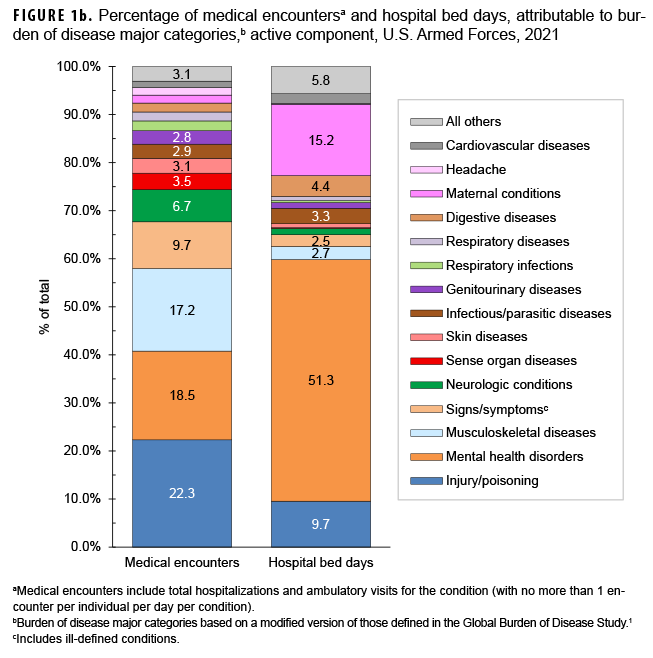
In 2021, more active component service members (individuals affected) (n=517,491) had medical encounters for injury/poisoning than any other morbidity-related category (Figure 1a). In addition, injury/poisoning accounted for more medical encounters (n=2,657,136) than any other morbidity category and over one-fifth (22.3%) of all medical encounters overall.
Mental health disorders accounted for more hospital bed days (n=179,986) than any other morbidity category and over half (51.3%) of all hospital bed days overall (Figures 1a, 1b). Together, injury/poisoning and mental health disorders accounted for over three-fifths (61.1%) of all hospital bed days and about two-fifths (40.8%) of all medical encounters.
Of note, maternal conditions (e.g., pregnancy complications and delivery) accounted for a relatively large proportion of all hospital bed days (n=53,295; 15.2%) but a much smaller proportion of medical encounters overall (n=197,106; 1.7%) (Figures 1a, 1b). Routine prenatal visits are not included in this summary.
Medical encounters, by condition
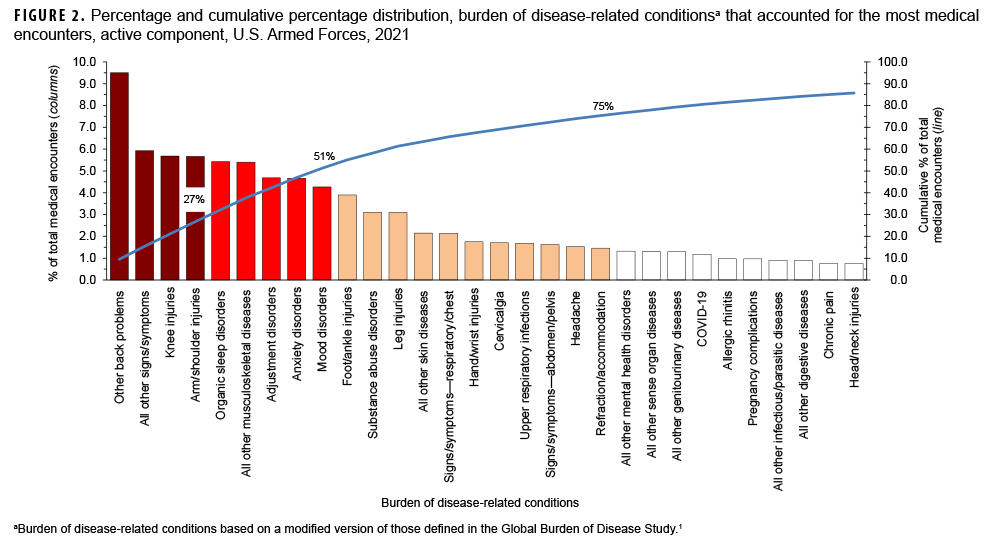
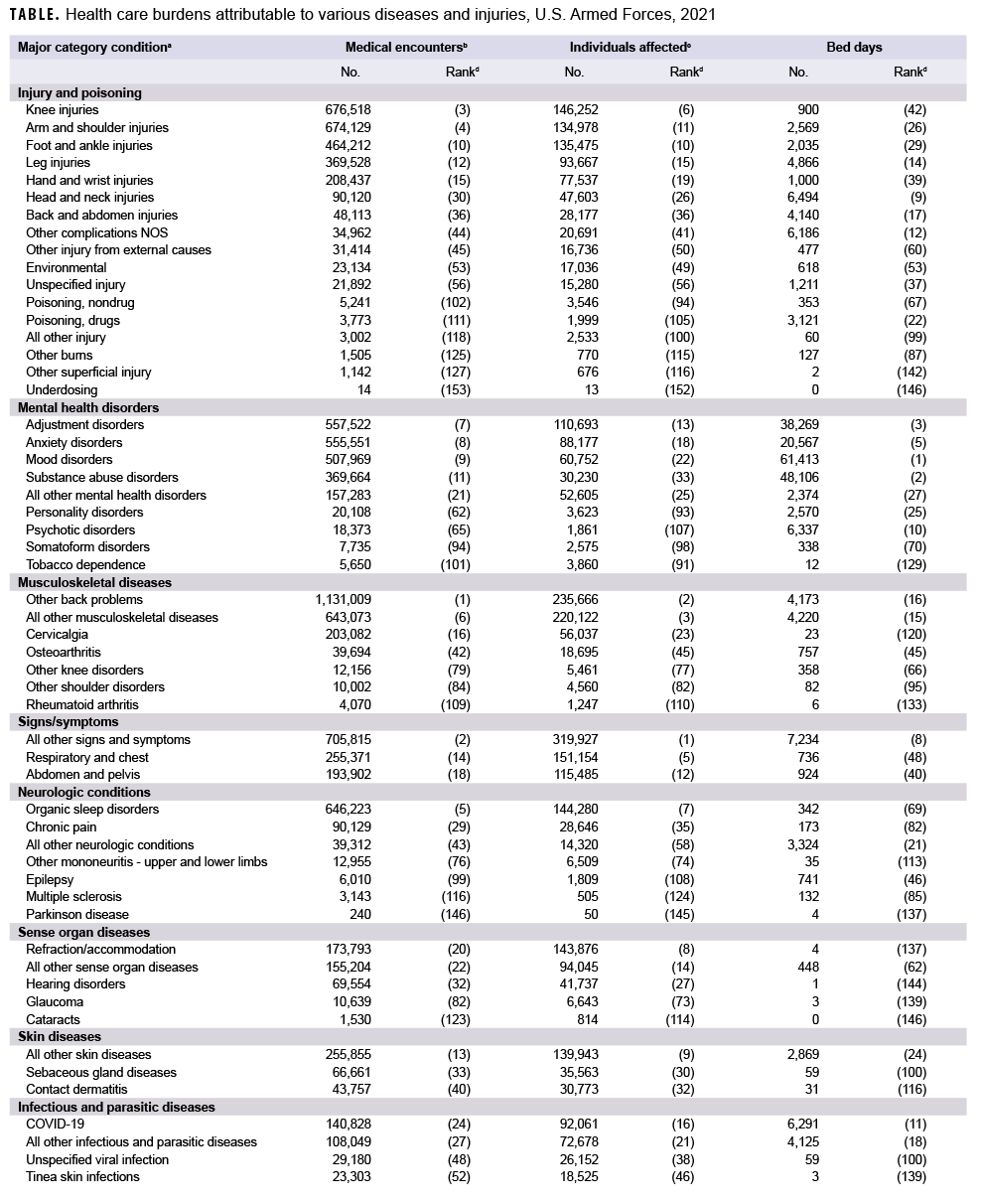
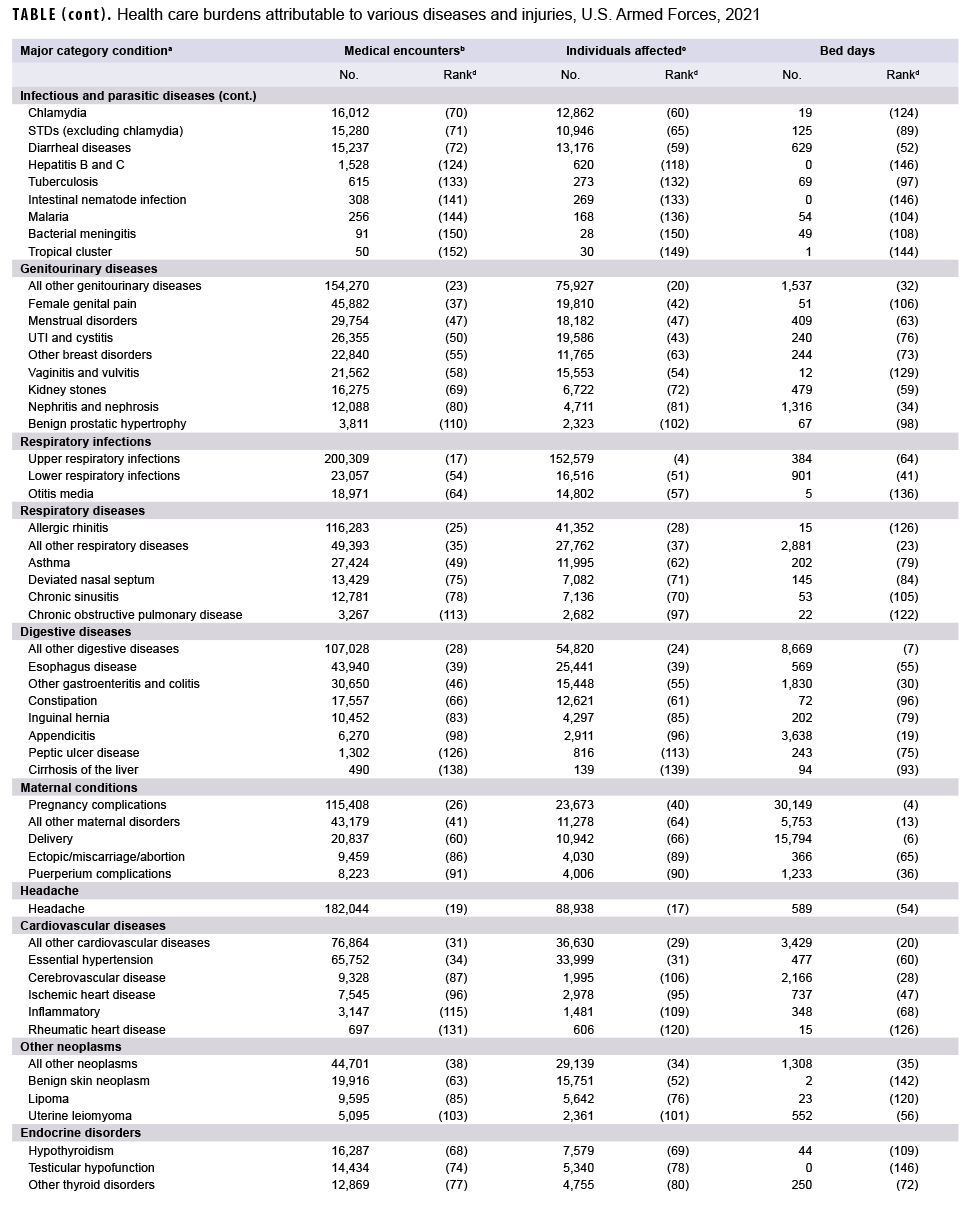
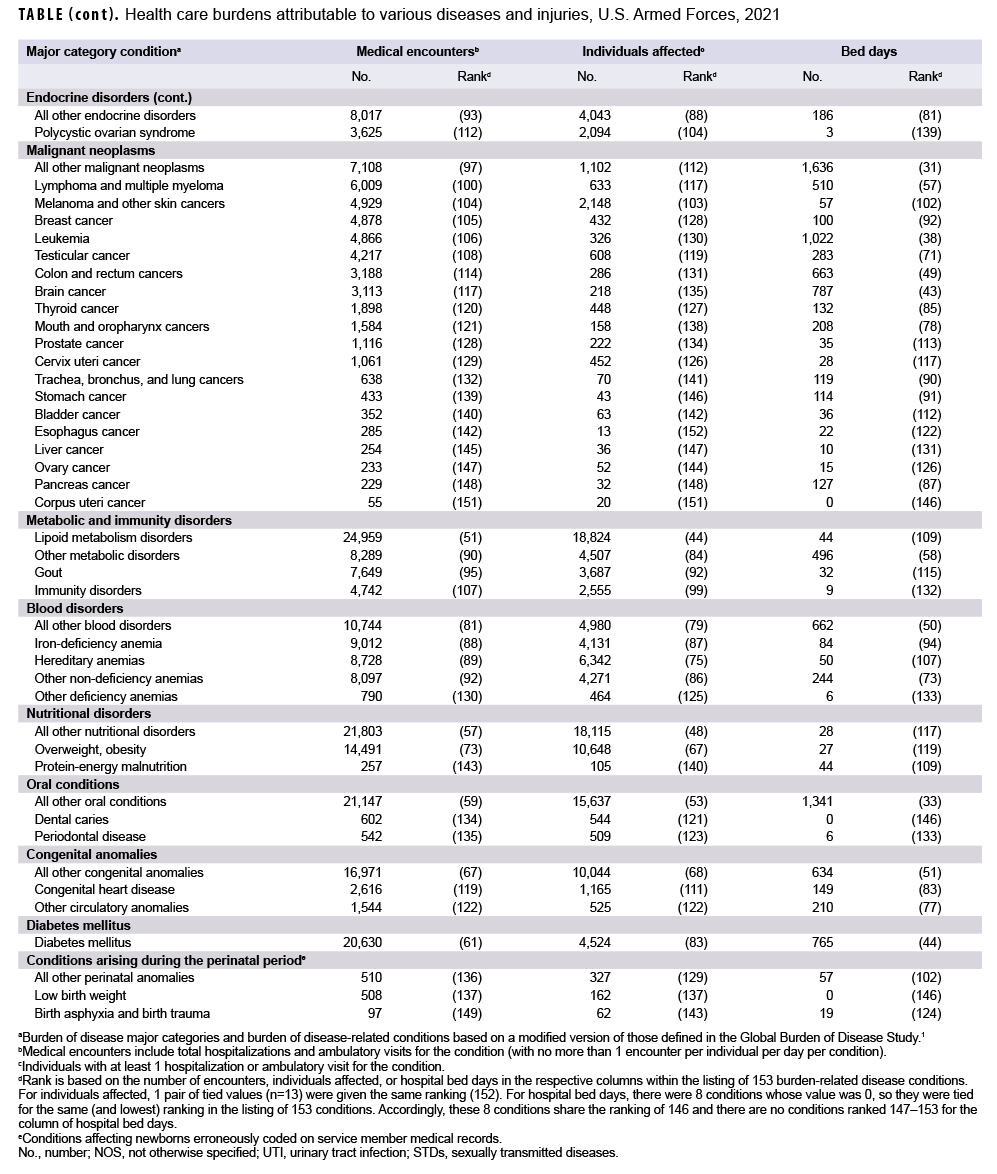
In 2021, the 3 burden of disease-related conditions that accounted for the most medical encounters were other back problems, all other signs and symptoms, and knee injuries. These conditions accounted for slightly more than one-fifth (21.1%) of all illness- and injury-related medical encounters overall (Figure 2). Moreover, the top 9 conditions associated with the most medical encounters accounted for more than half (51.2%) of all illness- and injuryrelated medical encounters overall. In general, the conditions that accounted for the most medical encounters among active component service members in 2021 were predominantly musculoskeletal diseases (e.g., back problems), injuries (e.g., knee, arm/shoulder, foot/ankle, or leg), mental health disorders (e.g., adjustment disorders, anxiety disorders, mood disorders, or substance abuse disorders), other signs and symptoms (e.g., dizziness and giddiness, palpitations), and organic sleep disorders (e.g., insomnia, organic sleep apnea) (Table, Figure 2). COVID-19 accounted for 1.2 percent of medical encounters and ranked 24th in total medical encounters during 2021 (Figure 2, Table).
Individuals affected, by condition
In 2021, more active component service members received medical care for all other signs and symptoms than for any other specific condition (Table). Of the top 10 conditions that affected the most service members, 2 were musculoskeletal diseases (other back problems and all other musculoskeletal diseases); 2 were injuries (knee and foot/ankle); 2 were signs and symptoms (all other signs and symptoms and respiratory and chest); 1 was respiratory infections (upper respiratory infections); 1 was a neurological condition (organic sleep disorders); 1 was a sense organ disease (refraction/accommodation); and 1 was skin diseases (all other skin diseases). A total of 92,061 active component service members received care for COVID-19, which ranked 16th in the number of service members affected as compared to all other conditions.
Hospital bed days, by condition
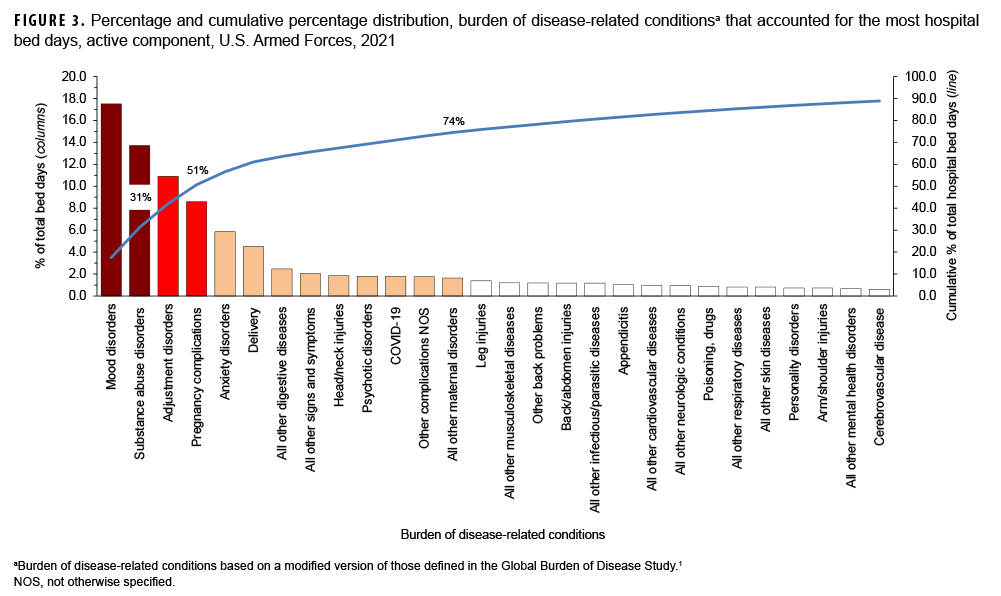
In 2021, mood and substance abuse disorders accounted for nearly one-third (31.2%) of all hospital bed days (Figure 3). Together, 4 mental health disorders (mood, substance abuse, adjustment, and anxiety) and 2 maternal conditions (pregnancy complications and delivery) accounted for more than three-fifths (61.1%) of all hospital bed days (Table, Figure 3). About 10 percent (9.7%) of all hospital bed days were attributable to injuries and poisonings. A total of 6,291 bed days were attributable to COVID-19 which was ranked 11th among all conditions for bed days (Table).
Relationships between health care burden indicators
There was a strong positive correlation between the number of medical encounters attributable to various conditions and the number of individuals affected by the conditions (r=0.87) (data not shown). For example, the 3 leading causes of medical encounters were among the 6 conditions that affected the most individuals (Table). In contrast, there were weak to moderate positive relationships between the hospital bed days attributable to conditions and either the numbers of individuals affected by (r=0.20) or medical encounters attributable to (r=0.41) the same conditions. For example, substance abuse disorders and labor and delivery were among the topranking conditions in terms of proportion of total hospital bed days; however, these conditions affected relatively few active component service members.
Editorial Comment
This report reiterates the major findings of prior annual reports on morbidity and health care burdens among U.S. military members. In 2021, as in prior years, the burden of disease categories of musculoskeletal diseases, injury and poisoning, mental health disorders, and maternal conditions accounted for relatively large proportions of the morbidity and health care burdens that affected active component service members. Of the 153 burden of disease-related conditions, just 9 (6.0%) accounted for slightly more than half of all illness- and injury-related medical encounters of active component members. These conditions included 2 musculoskeletal conditions (other back problems and all other musculoskeletal diseases), 2 anatomic sitedefined injuries (knee and arm/shoulder), organic sleep disorders, all other signs and symptoms, and 3 mental health disorders (adjustment, anxiety, and mood disorders). It is important to note that this pattern of illness and injury among U.S. active component members is distinctive from other population groups characterized by different demographic distributions and occupational hazards. Examples of such different populations include not only the general U.S. population but also other MHS beneficiaries such as family members and retirees. The differing burdens of disease and injury for the other MHS beneficiaries are described in another article in this issue of the MSMR.3
Although 2021 was impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic, COVID-19 accounted for relatively modest numbers of medical encounters, bed days, and service members affected as compared to other conditions included in this analysis. This is likely due to several factors including the robust mitigation measures employed by the DoD to prevent COVID-19 infections and the fact that active component service members represent a relatively young and healthy population.
Mental health disorders (including substance abuse disorders), injuries, and musculoskeletal disorders of the back have been leading causes of morbidity and disability among service members throughout military history.4–10 It is well recognized that the prevention, treatment, and rehabilitation of back problems and joint injuries, and the detection, characterization, and management of mental health disorders—including substance abuse and deployment stress-related disorders (e.g., post-traumatic stress disorder)—should be the highest priorities for military medical research, public health, and force health protection programs.
In summary, this analysis, similar to prior years, documents that relatively few illnesses and injuries account for a substantial proportion of morbidity and health care burdens that affect U.S. military members. Illnesses and injuries that disproportionately contribute to morbidity and health care burdens should be high-priority targets for preventive action, research, and resources.
References
- Murray CJL, Lopez AD, eds. The Global Burden of Disease: A Comprehensive Assessment of Mortality and Disability from Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors in 1990 and Projected to 2020. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1996:120–122.
- Brundage JF, Johnson KE, Lange JL, Rubertone MV. Comparing the population health impacts of medical conditions using routinely collected health care utilization data: nature and sources of variability. Mil Med. 2006;171(10):937–942.
- Armed Forces Health Surveillance Division. Absolute and relative morbidity burdens attributable to various illnesses and injuries, non-service member beneficiaries of the Military Health System, 2021. MSMR. 2022;29(6):xx–xx.
- Cozza KL, Hales RE. Psychiatry in the Army: a brief historical perspective and current developments. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1991;42(4):413–418.
- Watanabe HK, Harig PT, Rock NL, Koshes RJ. Alcohol and drug abuse and dependence. In: Jones FD, Sparcino, LR, Wilcox VL, Rotherberg JM, eds. Textbook of Military Medicine. Military Psychiatry: Preparing in Peace for War. Falls Church, VA: Office of the Surgeon General; 1994.
- Jones BH, Perrotta DM, Canham-Chervak ML, Nee MA, Brundage JF. Injuries in the military: a review and commentary focused on prevention. Am J Prev Med. 2000;18(3 suppl):71–84.
- Hoge CW, Auchterlonie JL, Milliken CS. Mental health problems, use of mental health services, and attrition from military service after returning from deployment to Iraq or Afghanistan. JAMA. 2006;295(9):1023–1032.
- Packnett ER, Elmasry H, Toolin CF, Cowan DB, Boivin MR. Epidemiology of major depressive disorder disability in the US military: FY 2007–2012. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2017;205(9):672–678.
- Update: Mental health disorders and mental health problems, active component, U.S. Armed Forces, 2016–2020. MSMR. 2021;28(8):2–9.
- Update: Mental health disorders and mental health problems, active component, U.S. Armed Forces, 2016–2020. MSMR. 2021;28(8)2–9.