Reportable Medical Events are documented in the Disease Reporting System internet by health care providers and public health officials throughout the Military Health System. The DRSi collects reports on over 70 different RMEs, including infectious and non-infectious conditions, outbreak reports, STI risk surveys, and tuberculosis contact investigations. These reports are reviewed by each service’s public health surveillance hub, which serves as an active primary prevention component to identify other service members at risk, assess need for post-exposure screening and prophylaxis, or inform other actions to protect and assure public health. Primary prevention (reducing disease occurrence) is the most effective method for preserving the medical readiness of the force.
Routine monitoring, evaluation, and publication of RMEs provide an important data resource for both policymakers and commanders, to guide their efforts for controlling and preventing diseases with potential measurable impacts on public health and force readiness—strategic, operational, and tactical. RMEs were chosen by consensus and recommendations from each service, which evaluated lists of nationally-notifiable diseases from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, position statements from the Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists, and other events identified as significant military health threats meriting added surveillance. A complete list of RMEs is available in the 2022 Armed Forces Reportable Medical Events Guidelines and Case Definitions.
The data presented in the table not only list the most recent case counts but reveal trends of incidence for the past two months, year-to-date, and over the preceding year.
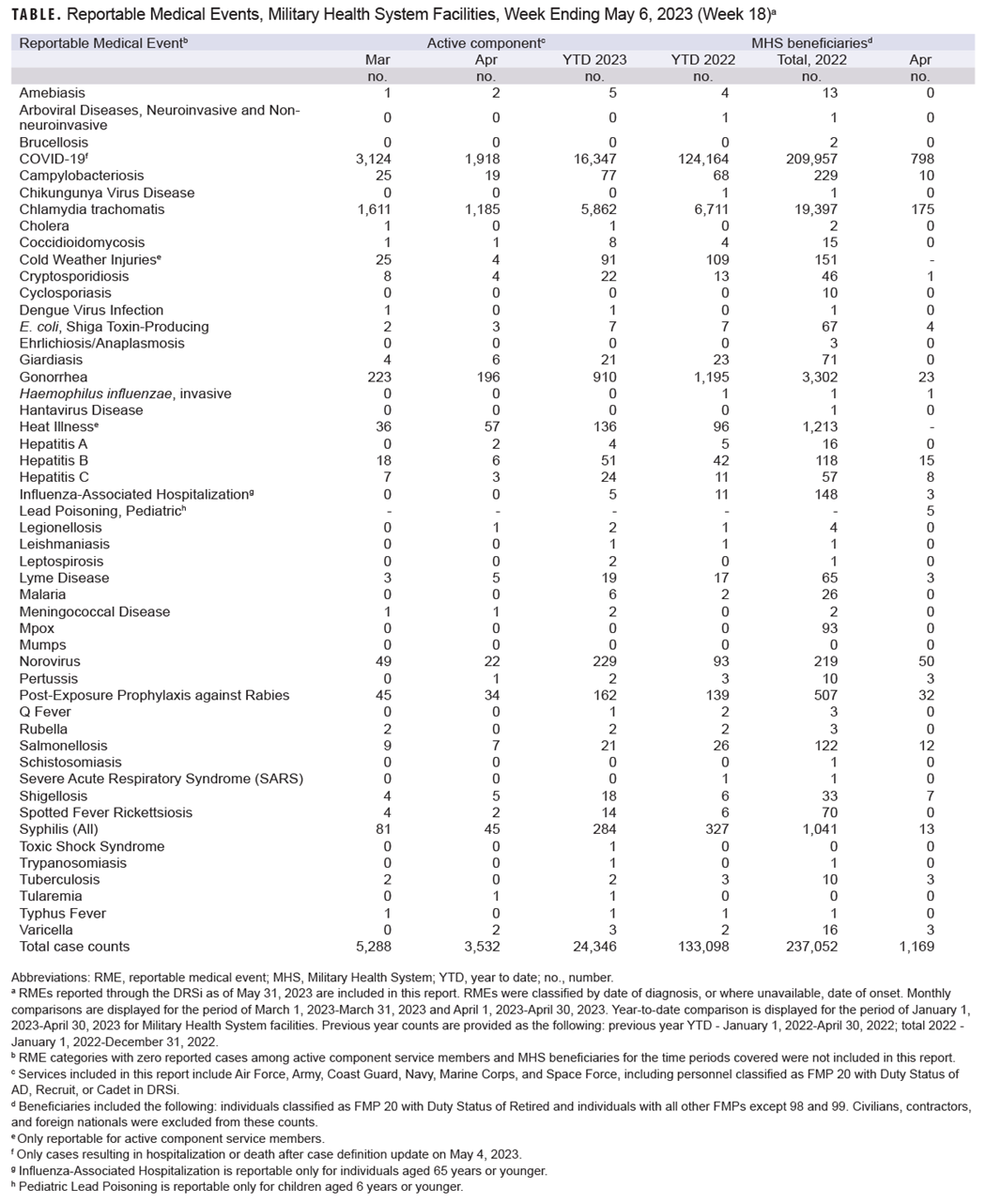
Data reported in the table are considered provisional and do not represent conclusive evidence until case reports are fully validated.
The most recent data on the five most frequent RMEs among total active component cases, as reported per week during the preceding year, are depicted in the Top 5 RME Trends by Calendar Week graph. COVID-19 is excluded from the graph due to 2023 changes in reporting and case definitions.