 HIV Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis is a highly effective medicine for preventing HIV when used as prescribed, reducing the risk of HIV from sex by around 99% and the risk of HIV from injection drug use by at least 74%.1 The Department of Defense follows the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention HIV PrEP guidelines for identification of individuals eligible for HIV PrEP and their evaluation and monitoring.2 This Surveillance Snapshot was created to determine the number of active component service members prescribed PrEP during 2023.
HIV Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis is a highly effective medicine for preventing HIV when used as prescribed, reducing the risk of HIV from sex by around 99% and the risk of HIV from injection drug use by at least 74%.1 The Department of Defense follows the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention HIV PrEP guidelines for identification of individuals eligible for HIV PrEP and their evaluation and monitoring.2 This Surveillance Snapshot was created to determine the number of active component service members prescribed PrEP during 2023.
Data from the Defense Medical Surveillance System were used for this analysis.3 The population was restricted to ACSMs who received a PrEP prescription between January 1, 2023 and December 31, 2023. A PrEP prescription was defined as a record in the Pharmacy Data Transaction System or Theater Medical Data Store medication files within DMSS containing the drug name Truvada, Descovy, Emtricitabine, Tenofovir, Apretude, or Cabotegravir. Records with the names Disoproxil, Viread, or Emtricitabine or listing a therapeutic class of 081808 (antiretrovirals) were excluded, as those are HIV treatment medications. Additionally, a prescription record was excluded if an individual had a diagnosis of chronic hepatitis B or HIV on or before the prescription date, or a needlestick diagnosis within 30 days before or after the prescription date.
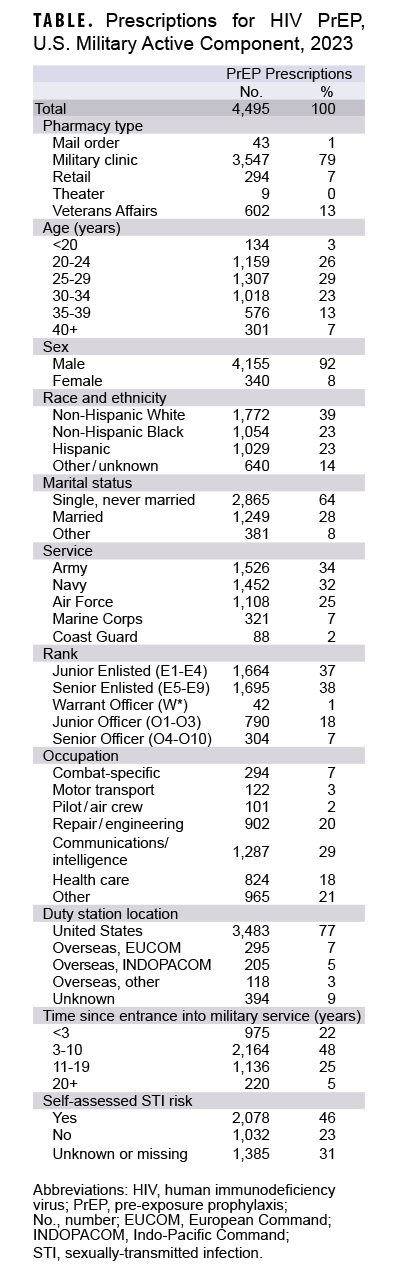
An individual was counted once during the surveillance year. Counts were summarized by pharmacy type, demographic characteristics, service-related variables, and self-assessed sexually-transmitted infection risk (defined from the Periodic Health Assessment if completed within one year prior to the prescription date) (Table).
There were 4,495 ACSMs with a prescription for HIV PrEP in 2023 (Table). The majority of prescriptions (79%) were obtained directly from a military clinic. The demographic groups with the highest numbers of prescriptions were 25-29 year olds (1,307), males (4,155), non-Hispanic Whites (1,772), and single, never married (2,865) ACSMs. In evaluating service-related characteristics, the highest number of prescriptions were among Army and Navy service members (1,526 and 1,452, respectively), enlisted (1,664 junior and 1,695 senior), communications/intelligence occupations (1,287), stationed in the U.S. (3,483), and in service for 3-10 years (2,164). The majority of service members with a prescription had a self-assessed risk for a STI (46%), but this information was unknown for 31% of the total PrEP recipients.
These data provide an overview of ACSMs receiving HIV PrEP in 2023 and can be used to further evaluate subpopulations within the ACSM population that may have a missed opportunity for receiving HIV PrEP.
Authors’ Affiliation
Epidemiology and Analysis Branch, Armed Forces Health Surveillance Division, Defense Health Agency: Dr. Eick-Cost, Dr. Mabila, and Dr. Ying
Disclaimer
The contents of this publication are the sole responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views, assertions, opinions, nor policies of the Defense Health Agency or the Department of Defense.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP). Accessed Feb. 26, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/risk/prep/index.html
- Defense Health Agency. Defense Health Agency Procedural Instruction 6025.29: Provision of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) for Persons at High Risk of Acquiring HIV Infection. Department of Defense. Updated Dec. 20, 2019. Accessed Feb. 26, 2024. https://www.health.mil/Reference-Center/DHA-Publications/2019/12/20/DHA-PI-6025-29
- Rubertone MV, Brundage JF. The Defense Medical Surveillance System and the Department of Defense serum repository: glimpses of the future of public health surveillance. Am J Public Health. 2002;92(12):1900-1904.