MHS operational innovations continue in battle against COVID-19
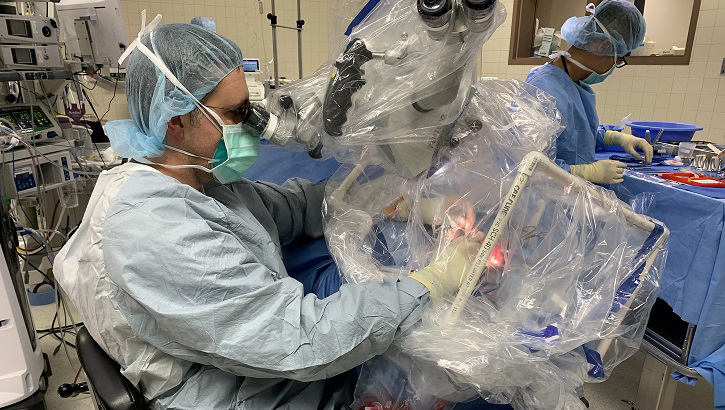 Army Maj. (Dr.) Douglas Ruhl, a surgeon at Madigan Army Medical Center, at Joint Base Lewis-McChord, Washington, uses the COVID-19 airway management isolation chamber (CAMIC) to perform a mastoidectomy, which removes a growth behind the eardrum. This procedure requires drilling into the skull, creating bone dust and aerosolized droplets. (Photo courtesy of Douglas Ruhl.)
Army Maj. (Dr.) Douglas Ruhl, a surgeon at Madigan Army Medical Center, at Joint Base Lewis-McChord, Washington, uses the COVID-19 airway management isolation chamber (CAMIC) to perform a mastoidectomy, which removes a growth behind the eardrum. This procedure requires drilling into the skull, creating bone dust and aerosolized droplets. (Photo courtesy of Douglas Ruhl.)
Operational medicine performed by deployed military medical personnel has always driven innovation, and this was more important than ever in responding to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Military Health System innovations in 2020 include a new registry for real-time COVID-19 data and a system to free up hospital beds and protect patients from the disease. Service Members also developed inexpensive ventilator designs and adapted safer ways to transport and perform surgical procedures on COVID-19 patients.
Meeting the need for real-time COVID-19 data, the Joint Trauma System (JTS) developed a global COVID-19 registry to track patients and their outcomes.
The COVID-19 registry exceeded 90,000 patients in the Department of Defense as of the first week of December, said JTS Chief, Air Force Col. (Dr.) Stacy Shackelford. The registry began collecting real-time COVID-19 data in May.
The JTS is conducting detailed patient chart analyses of the COVID-19 registry to look at items such as deaths within the MHS and other COVID-19 subpopulations of interest, Shackelford said. So far, 3,200 charts have been analyzed.
“In general, the registry has an important capability to look at treatments and outcomes. That’s our number one goal,” she said. For example, the registry compares outcomes of COVID-19 available treatments including convalescent plasma, steroids and remdesivir.
“Our number two goal is long-term tracking of patients and links to other outcomes,” Shackelford said.
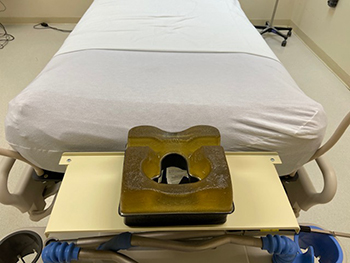 A pronating shelf (foreground) was designed to improve a COVID-19 patient’s ability to breathe through a ventilator while face down in an ICU bed. The shelf, with cutouts for a patient’s face, was prototyped at Keesler Air Force Base, Mississippi. (Photo courtesy of Keesler Air Force Base.)
A pronating shelf (foreground) was designed to improve a COVID-19 patient’s ability to breathe through a ventilator while face down in an ICU bed. The shelf, with cutouts for a patient’s face, was prototyped at Keesler Air Force Base, Mississippi. (Photo courtesy of Keesler Air Force Base.)
The registry could track active duty personnel’s annual physical fitness tests for lingering COVID-19-related results, or the annual periodic health assessment, to which the JTS plans to add questions related to mental health and the COVID-19 pandemic, she added. Additionally, “the registry is tracking genetics testing down to the granular level so we can tap into a look at clinical outcomes that would be available to other scientists.”
Members also developed innovative ways to modify the care environment to meet the needs of COVID-19 patients, like a pronating shelf and a low-cost ventilator.
The pronating shelf, prototyped at Keesler Air Force Base in Mississippi, helps COVID-19 patients breathe while lying prone (face down) for hours while on ventilators. Previously, patients in this position using a ventilator had their head and neck turned at a difficult angle, which often obstructed airways. The Keesler pronate shelf supports the head while keeping it in proper position to use the ventilator.
The Naval Surface Warfare Center Panama City Division (NSWC PCD) in Florida developed low-cost, easily-assembled ventilators to expand access to these life-saving devices. The ventilators were designed as part of a challenge across hundreds of submissions and entered the prototype phase.
The challenge came during the initial surge in the pandemic, and the Navy ventilators were intended as stop-gap measures should ventilator supplies have dwindled across the nation or if COVID-19 numbers surged beyond U.S. hospitals’ capacities. These units were tested at the Walter Reed National Military Medical Center (WRNMMC) in Bethesda, Maryland.
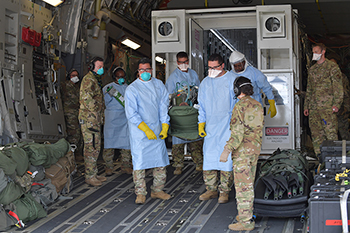 Airmen assigned to the 313th Expeditionary Operations Support Squadron transfer a COVID-19 patient following the first-ever operational use of the Negatively Pressurized Conex to transport 12 patients aboard a C-17 Globemaster III aircraft at Ramstein Air Base, Germany on July 1, 2020 to receive higher level of care at the Landstuhl Regional Medical Center, Germany. The NPC is the latest isolated containment chamber developed to transport up to 28 individuals with infectious diseases. (Photo by Air Force Airman 1st Class John Wright.)
Airmen assigned to the 313th Expeditionary Operations Support Squadron transfer a COVID-19 patient following the first-ever operational use of the Negatively Pressurized Conex to transport 12 patients aboard a C-17 Globemaster III aircraft at Ramstein Air Base, Germany on July 1, 2020 to receive higher level of care at the Landstuhl Regional Medical Center, Germany. The NPC is the latest isolated containment chamber developed to transport up to 28 individuals with infectious diseases. (Photo by Air Force Airman 1st Class John Wright.)
The first commercially produced version of the Navy’s PRE-Vent is being built for a final round of U.S. Food and Drug Administration testing that aims to prove the design can be manufactured from biocompatible materials and pass stringent agency guidelines for emergency use authorization. The build should be completed this January and then sent for evaluation to the FDA.
The ventilators can be assembled from materials commonly found at hardware stores with a cost of $300 to $600, significantly less than commercially available ventilators. The ventilators can be built on the fly to address patients’ breathing assistance needs in field hospital settings.
Transporting COVID-19 patients by air led to another innovation to protect patients, providers and aircrew during flight.
The Air Force’s Negatively Pressurized Conex (NPC) allows for the safe air transport of patients exposed to COVID-19 without risking the aircrew’s health by surrounding patients within a negatively pressurized containment system. This system allows for the transport of up to 24 infected personnel seated or up to eight stretchers. Thus far during this global pandemic, the Air Force has successfully completed some 65 COVID-19 aeromedical evacuation missions.
The need to protect health care workers from COVID-19 led to the development of the COVID-19 Airway Management Isolation Chamber, or CAMIC. CAMIC is a an adjunct personal protective equipment (PPE) barrier device constructed by placing a large clear plastic bag on a PVC piping box frame over the head, neck and shoulders of patients. When used with other PPE, CAMIC protects health care personnel by providing a physical barrier to aerosolized droplets from patients with COVID-19 by capturing and removing viral particles emitted by the patient. CAMIC was conceived, designed, built and tested by the Army’s Telemedicine and Advanced Technology Research Center.
In a similar vein, researchers from the U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command’s Army Research Laboratory and the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center created an individual biocontainment unit that uses negative pressure to suction the air from around a patient and filter out viral particles.
While 2020 proved to be an active year for operational medical innovations because of the global pandemic, the MHS continuously develops creative protocols, systems or devices that can be used in austere environments where energy sources are limited and where the military is deployed.