Reportable Medical Events are documented in the Disease Reporting System internet by health care providers and public health officials throughout the Military Health System to monitor, control, and prevent the occurrence and spread of diseases of public health interest or readiness importance. These reports are reviewed by each service’s public health surveillance hub. The DRSi collects reports on over 70 different RMEs, including infectious and non-infectious conditions, outbreak reports, STI risk surveys, and tuberculosis contact investigation reports. A complete list of RMEs is available in the 2022 Armed Forces Reportable Medical Events Guidelines and Case Definitions.1 Data reported in these tables are considered provisional and do not represent conclusive evidence until case reports are fully validated.
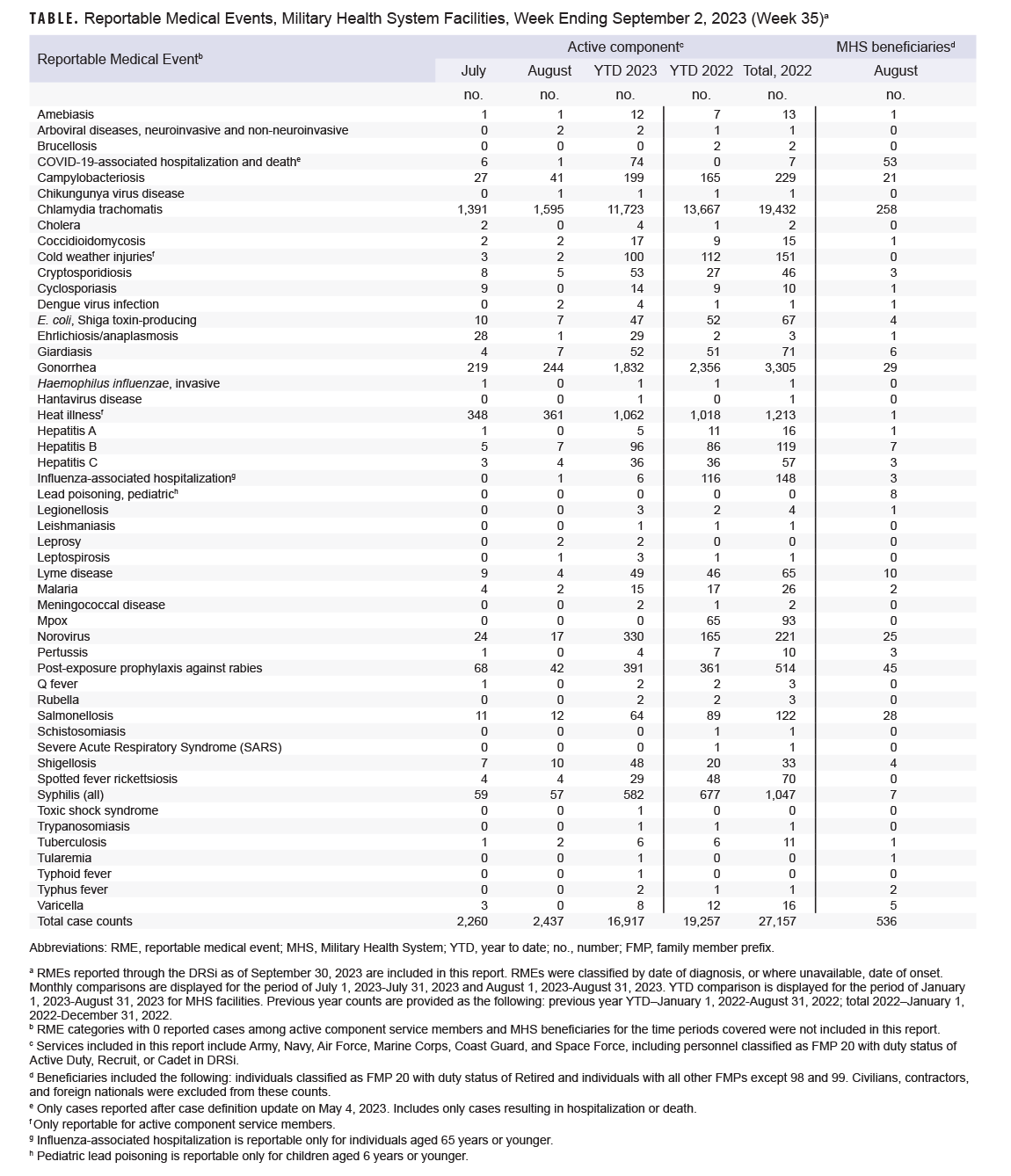
Total active component cases reported per week are displayed for the top five RMEs for the previous year. Each month, the graph is updated with the five most frequently occurring RMEs, to present the most recent month’s (August 2023) five most frequent RMEs, which may differ from previous months. COVID-19 is excluded from these graphs due to changes in reporting and case definition updates in 2023.
For questions about this report, please contact the Disease Epidemiology Branch at the Defense Centers for Public Health–Aberdeen, email: dha.apg.pub-health-a.mbx.disease-epidemiologyprogram13@health.mil.
Author Affiliations
Defense Centers for Public Health–Aberdeen, Disease Epidemiology Branch
References
- Armed Forces Health Surveillance Division. Armed Forces Reportable Medical Events. Accessed Sept. 6, 2023. https://health.mil/Reference-Center/Publications/2022/11/01/Armed-Forces-Reportable-Medical-Events-Guidelines
- Defense Manpower Data Center. Department of Defense Active Duty Military Personnel by Rank/Grade of Service, October 31, 2022. https://dwp.dmdc.osd.mil/dwp/app/dod-data-reports/workforce-reports
- Defense Manpower Data Center. Armed Forces Strength Figures for January 31, 2023. https://dwp.dmdc.osd.mil/dwp/app/dod-data-reports/workforce-reports
- Navy Medicine. Surveillance and Reporting Tools—DRSI: Disease Reporting System Internet. https://www.med.navy.mil/Navy-Marine-Corps-Public-Health-Center/Preventive-Medicine/Program-and-Policy-Support/Disease-Surveillance/DRSI