Each year, the MSMR estimates illness- and injury-related morbidity and health care burdens on the U.S. Armed Forces and the Military Health System, and this report updates previous analyses of these burden distributions among active and reserve component service members in deployed settings. While deployed service members are primarily selected from a subset of the active component, the reserve component also contributes a substantial portion of U.S. deployed forces. This report focuses on the health encounters of service members during deployment to two specific theaters of operation: U.S. Central Command (CENTCOM) and U.S. Africa Command (AFRICOM). While U.S. service members are deployed to all geographic combatant commands, the largest concentrations without access to fixed medical facilities are in the CENTCOM and AFRICOM areas of operation.1
This report utilizes data from the Theater Medical Data Store, which documents service members’ inpatient and outpatient encounters while treated in an operational environment; MHS GENESIS captures health care data at permanent military facilities. TMDS receives medical data from Theater Medical Information Program-Joint applications, including AHLTA-Theater, TMIP-Composite Health Care System Cache, Mobile Computing Capability, Maritime Medical Modules, and the U.S. Transportation Command Regulating and Command and control Evacuation System (TRAC2ES).2
While this report focuses on medical encounters of service members treated in CENTCOM and AFRICOM operational environments during the 2022 calendar year, future reports may incorporate other combatant commands as circumstances dictate and data become available.
What are the new findings?
Administrative and other health services (ICD-10 “Z” codes) together with musculoskeletal disorders accounted for more than half of total medical encounters in 2022 among service members deployed to the U.S. Central Command (CENTCOM) or the U.S. Africa Command (AFRICOM). Three common injury conditions—other back problems, arm/shoulder injuries, and knee injuries—were shared by male and female service members deployed to CENTCOM and AFRICOM.
What is the impact on readiness and force health protection?
Understanding the most common causes of injury and illness during deployment will help senior leaders develop and implement strategies to reduce preventable medical issues, preserving the fighting strength and enhancing readiness.
Methods
The surveillance population includes all individuals who served in the active or reserve components of the U.S. Army, Navy, Air Force, or Marine Corps with health care encounters captured in the TMDS during the surveillance period. This analysis was restricted to encounters where the theater of care specified was CENTCOM or AFRICOM, or where the name of the theater of operation was missing or null; by default, this excluded encounters in the U.S. Northern Command, U.S. European Command, U.S. Indo-Pacific Command, or U.S. Southern Command theaters of operations. In addition, TMDS-recorded medical encounters where the data source was identified as Shipboard Automated Medical System, or where the military treatment facility descriptor indicated that care was provided aboard a ship, were excluded from this analysis. Encounters from aeromedical staging facilities outside of CENTCOM or AFRICOM were also excluded.
Inpatient and outpatient medical encounters were summarized according to the primary (first-listed) diagnoses (if reported with an International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision [ICD-10] code between A00 and U09 and Z codes, excluding Z37). TMDS has not fully transitioned to ICD-10 codes, so some ICD-9 codes were included. Primary diagnoses that did not correspond to an ICD-9 or ICD-10 code are not reported in this burden analysis. Medical encounters were summarized by ICD code chapters, plus an additional category for separate classification of COVID-19 diagnoses.
Morbidity burdens attributable to various conditions were estimated by the distribution of diagnoses corresponding to the 17 traditional categories of the ICD system, with an 18th category for COVID-19. Extended ICD-10 code groupings were also reviewed for the most common diagnoses.
Results
In 2022, 48,446 individuals initiated a total of 136,009 medical encounters while deployed to Africa and Southwest Asia/Middle East. Of the 136,009 total medical encounters, 231 (0.17%) were recorded as hospitalizations. Most medical encounters (75.8%), individuals affected (80.0%), and hospitalizations (74.5%) occurred among male service members (data not shown).
In 2022, the largest percentages of medical encounters attributable to a major ICD-10 diagnostic category were coded as administrative and other health services (Z codes; includes factors influencing health status and health service contact), followed by musculoskeletal system/connective tissue disorders (Figure).
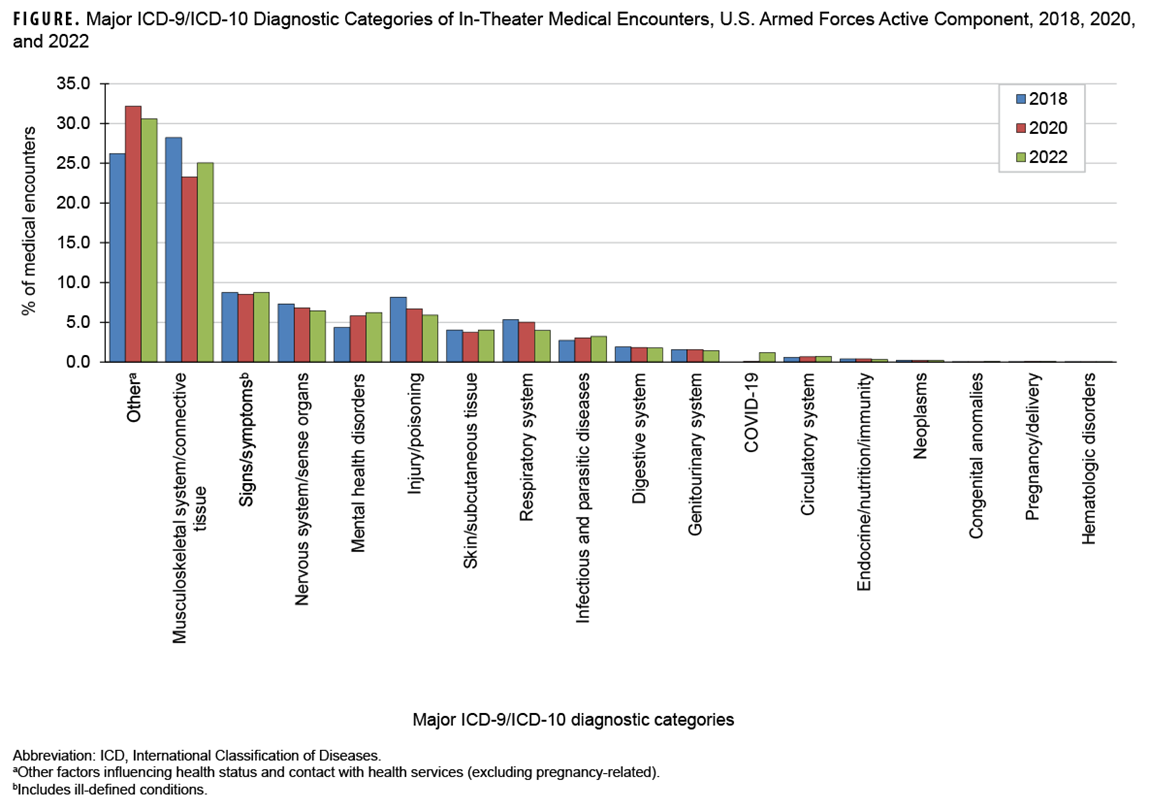
The percentage of total medical encounters attributed to other health services increased from 26.2% in 2018 to 30.6% in 2022, when the most common ICD-10 diagnoses in this category included Z1152 (COVID-19 screening, 4.6%), Z0289 (other administrative examinations, 4.3%), and Z5682 (military deployment status, 2.6%). COVID-19 accounted for 1.2% of all medical encounters in 2022 (Table).
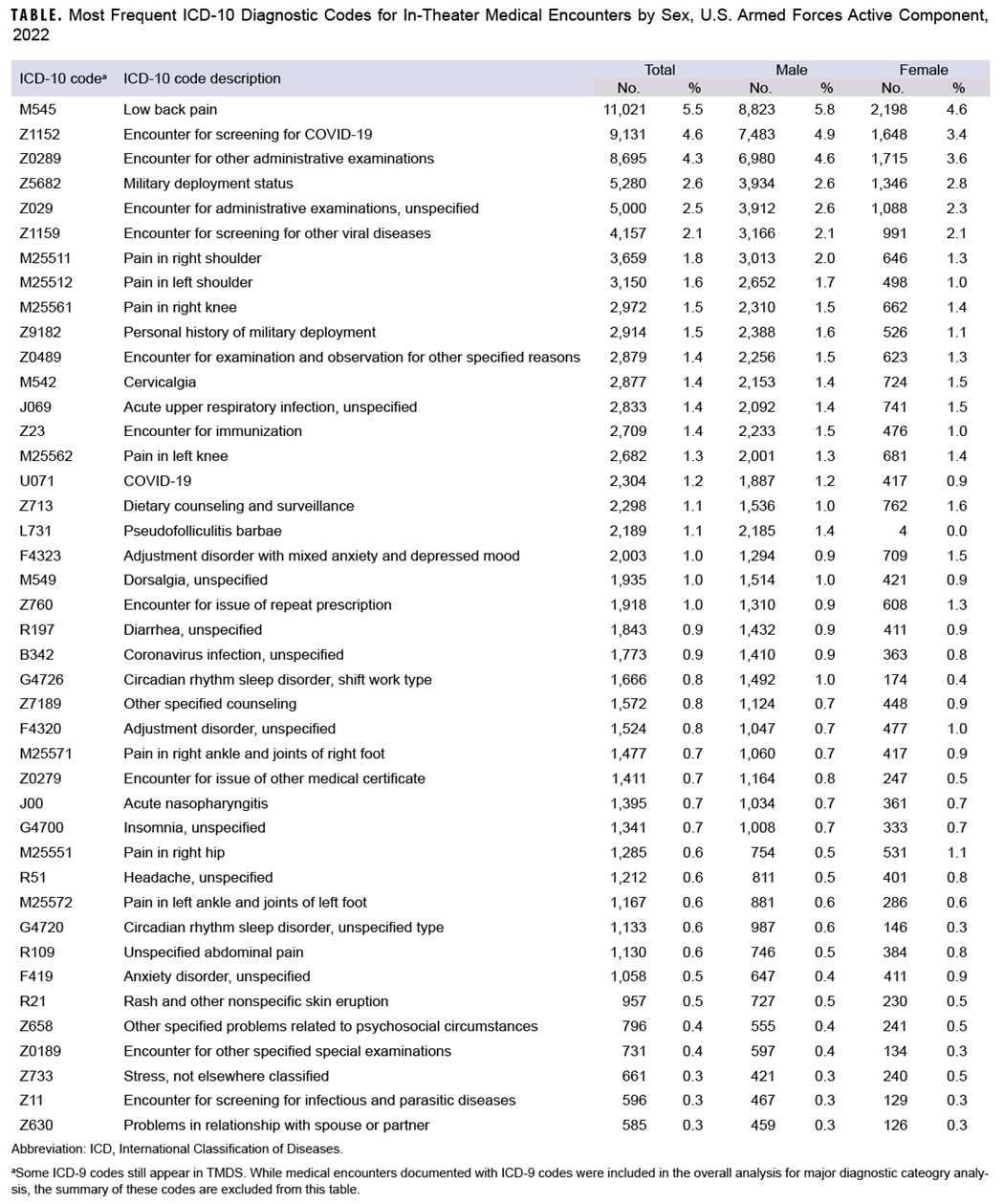
From 2018 to 2022, the percentage of in-theater medical encounters due to musculoskeletal disorders (28.2% to 25.1%) and injury (8.2% to 5.9%) decreased (Figure). Lower back pain (M545) was the most frequent diagnostic code for musculoskeletal encounters in both men and women, followed by pain in the right shoulder (M25511), pain in the left shoulder (M25512), pain in the right knee (M25561), and pain in the left knee (M25562) (Table).
The percentage of in-theater medical encounters attributed to mental health disorders increased from 4.4% to 6.2% during the surveillance period (Figure). Adjustment disorder with mixed anxiety and depressed mood (F4323) was the most frequent mental health disorder diagnosis, with a higher percentage of in-theater encounters for this disorder among women (1.5%) than men (0.9%) (Table).
Discussion
As in prior annual reports of illness- and injury-related morbidity and health care burdens in deployed settings, administrative and other health services together with musculoskeletal disorders accounted for more than half of total medical encounters in theater. COVID-19 screening may have partially contributed to the increase in encounters for administrative and other health services during the surveillance period, as this specific Z-code (Z1152) accounted for almost 5% of all in-theater medical encounters in 2022.
This report documents an increased percentage of mental health disorder medical encounters in theater, which is consistent with the 2018-2022 increased rate of ambulatory encounters for mental health disorders in garrison. The distribution of ambulatory encounters for mental health disorders in garrison (13.0%), however, was substantially higher than the percentage observed in theater (1.0%).3 No absolute rate comparisons can be made due to the lack of denominator (person-time) data in theater.
Encounters for certain conditions are generally rare in deployment settings. Some conditions, including diabetes, pregnancy, or congenital anomalies, often preclude deployment for service members. As a result of pre-screening, deployed service members demonstrate a lower rate of medical conditions that may interfere with deployment operations than their non-deployed counterparts. Deployed service members are also less likely to require medical care for pre-screened conditions.
Several limitations of the data presented in this report should be considered when interpreting these results and analyses. Not all medical encounters in theaters of operation are recorded in the TMDS. Some care by in-theater medical personnel occurs at small, remote, or austere forward locations where electronic documentation of diagnoses and treatment is infeasible, and some emergency medical care to stabilize combat-injured service members before evacuation may not be routinely captured in the TMDS. Due to the exigencies of deployment settings that complicate accurate data reporting or transmission, this report may underestimate the true burden of health care in the areas of operation examined.
In any review relying on ICD coding, some misclassification of diagnoses should be expected due to coding errors in the electronic health record. Although the aggregated distributions of illnesses and injuries presented in this report are compatible with expectations derived from other examinations of morbidity in military populations (both deployed and non-deployed), instances of highly unlikely diagnostic codes based on the deployed population have been observed. This misclassification bias is likely minor and non-differential.
The DOD does not maintain complete data to monitor personnel tempo data, which limits assessment of the amount of time service members are deployed or assigned to serve away from home for other events.4 This lack of denominator data for person-time makes direct comparison of numbers and percentages of medical evacuations by cause difficult.
This report only includes CENTCOM and AFRICOM medical encounters, and thus does not describe any medical encounters from the recent deployment of troops to the U.S. European Command (EUCOM), the U.S. Indo-Pacific Command (INDOPACOM), and the U.S. Southern Command (SOUTHCOM). Each area of operation is unique, with vastly different medical assets and numbers of deployed service members. The results from CENTCOM or AFRICOM may not be generalizable to other combatant commands.
References
- White House Briefing Room. Letter to the Speaker of the House and President Pro Tempore of the Senate Regarding the War Powers Report. December 8, 2022. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/statements-releases/2022/12/08/letter-to-the-speaker-of-the-house-and-president-pro-tempore-of-the-senate-regarding-the-war-powers-report-4
- Joint Operational Medicine Information Systems Program Management Office. TMDS Fact Sheet. Accessed July 18, 2023. https://www.health.mil/Reference-Center/Fact-Sheets/2019/07/30/TMDS-Fact-Sheet
- Armed Forces Health Surveillance Division. Ambulatory visits among active component members, U.S. Armed Forces, 2022. MSMR. 2023;30(6):19-25.
- United States Government Accountability Office. Report to Congressional Committees. GAO-18-253, Military Readiness: Clear Policy and Reliable Data Would Help DOD Better Manage Service Members’ Time Away from Home. April 2018. Accessed July 5, 2023. https://www.gao.gov/assets/gao-18-253.pdf