Pseudofolliculitis barbae, also known as “razor bumps” or “shaving bumps,” results from an inflammatory, foreign body reaction of the skin, caused by shortened and sharpened hair piercing to the epidermis and dermis.1 While PFB can affect any person who regularly shaves, literature demonstrates an increased prevalence for persons with tightly curly hair, particularly African American and Hispanic individuals, including service members in the U.S. military.1-3 Current grooming standards in the U.S. military mandate facial shaving to ensure adequate fitting and sealing of protective masks.1 A shaving waiver may be issued for medical reasons such as PFB, or for religious reasons, among others.1,4
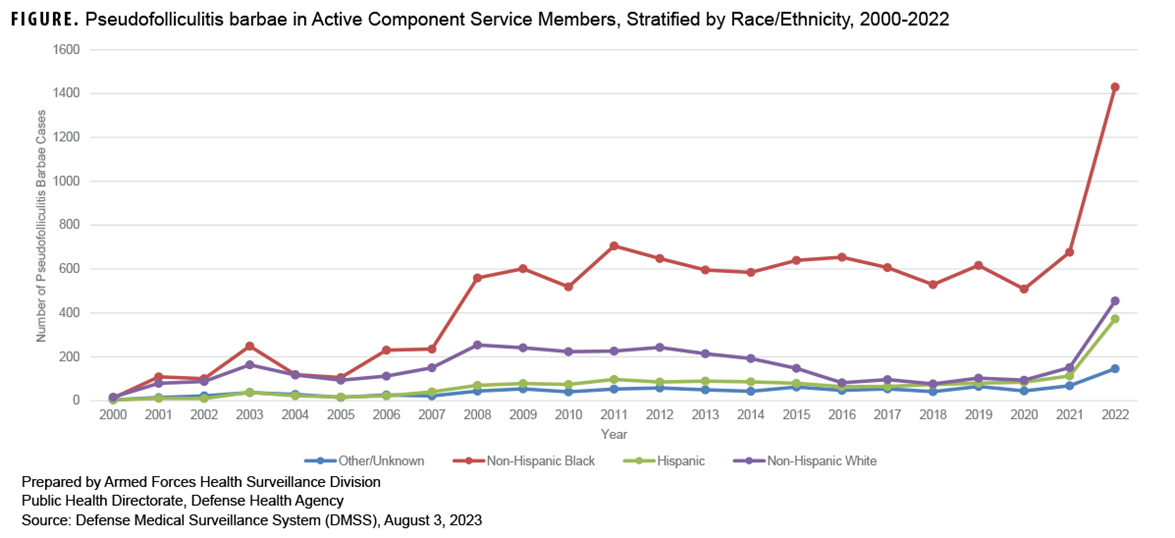
This Surveillance Snapshot describes the frequency of PFB cases among active component service members of the U.S. military from 2000 through 2022. A PFB case was counted once per year if the ACSM demonstrated either two outpatient or theater medical data store encounters within 60 days, or one inpatient encounter within the year. Overall, the frequency of PFB cases increased over the surveillance period and varied greatly by race/ethnicity, disproportionally affecting Non-Hispanic Black service members (Figure). Non-Hispanic Blacks, who have historically comprised 16-18% of the U.S military in the past 20 years,5-7 constitute a majority (63.5%) of PFB cases. The frequency trend is well out of proportion to the change in troop strength. The increase in reported cases from 50 in 2000 to 2,404 in 2022 may warrant further study.
References
- Tshudy T, Cho S. Pseudofolliculitis barbae in the U.S. military, a review. Mil Med. 2021;186(1-2):52-57. https://doi.org/10.1093/milmed/usaa243
- Perry P, Cook-Bolden F, Rahman Z, Jones E, Taylor S. Defining Pseudofolliculitis barbae in 2001: a review of the literature and current trends. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46(2):113-119. https://doi.org/10.1067/mjd.2002.120789
- Gelman A, Norton S, Valdes-Rodriguez R, Yosipovitch G. A review of skin conditions in modern warfare and peacekeeping operations. Mil Med. 2015;180(1):32-37. https://doi.org/10.7205/MILMED-D-14-00240
- Department of Defense. DoD Instruction 1300.17: Religious Liberty in the Military Services. 2020. Accessed August 1, 2023. https://www.esd.whs.mil/Portals/54/Documents/DD/issuances/dodi/130017p.pdf
- Barroso A. The changing profile of the U.S. military: smaller in size, more diverse, more women in leadership. 2019. Pew Research Center. Accessed August 2, 2023. https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2019/09/10/the-changing-profile-of-the-u-s-military
- Department of Defense. 2017 Demographics Profile of the Military Community. 2017. Accessed August 2, 2023. https://download.militaryonesource.mil/12038/MOS/Reports/2017-demographics-report.pdf
- Department of Defense. 2021 Demographics Profile of the Military Community. 2021. Accessed August 2, 2023. https://download.militaryonesource.mil/12038/MOS/Reports/2021-demographics-report.pdf
Author Affiliations
Defense Health Agency, Armed Forces Health Surveillance Division, Epidemiology and Analysis Section