Skip subpage navigation
Mpox Vaccine Resource Center
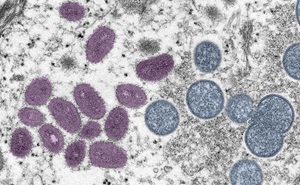 Mpox is a contagious disease caused by infection with the mpox virus. The mpox virus is an Orthopoxvirus and one of four that can infect humans; variola (which causes smallpox), vaccinia (used in the smallpox and mpox vaccine), and cowpox. It is a zoonotic disease, which means it can spread from animals to humans. It can also spread from person-to-person principally through direct contact with rash, scabs, body fluid, and to a lesser extent, respiratory secretions or by touching items previously in contact with the rash or body fluids. Anyone can be infected by mpox, and the CDC is providing information to a wide audience about symptoms and the behaviors that can lead to the spread of mpox. However, some communities are impacted more than others. To learn more, read the information provided by the CDC.
Mpox is a contagious disease caused by infection with the mpox virus. The mpox virus is an Orthopoxvirus and one of four that can infect humans; variola (which causes smallpox), vaccinia (used in the smallpox and mpox vaccine), and cowpox. It is a zoonotic disease, which means it can spread from animals to humans. It can also spread from person-to-person principally through direct contact with rash, scabs, body fluid, and to a lesser extent, respiratory secretions or by touching items previously in contact with the rash or body fluids. Anyone can be infected by mpox, and the CDC is providing information to a wide audience about symptoms and the behaviors that can lead to the spread of mpox. However, some communities are impacted more than others. To learn more, read the information provided by the CDC.
The first human case of mpox was recorded in 1970. It is endemic in several Central and West African countries. Prior to the 2022 outbreak, nearly all mpox cases in people outside of Africa were linked to international travel to countries where the disease commonly occurs, or through imported animals. The current outbreak outside of Africa involves a different strain of mpox virus that causes a less severe illness.
Patients with mpox may experience fever, swollen lymph nodes, malaise, headache and muscle aches followed by onset of a rash that develops into pustular skin lesions. Not everyone with mpox develops all of the symptoms. A person is considered infectious from the onset of illness until all lesions have crusted over and those scabs have separated revealing a layer of healthy skin.
In 2019, FDA licensed JYNNEOS, a replication-deficient Modified Vaccinia Ankara vaccine, for prevention of smallpox or mpox disease in adults aged ≥18 years determined to be at high risk for infection with these viruses.
You will find below all of the resources you will need about the mpox vaccine. More will be added as they are published or released.
You also may be interested in...
Publication
Jun 7, 2024
 .PDF |
107.82 KB
.PDF |
107.82 KB
Updated utilization and ordering guidance for the Jynneos Vaccine, to maximize the use of available vaccine for Mpox prevention.
Fact Sheet
Aug 16, 2022
This Fact Sheet is for healthcare providers administering vaccine and contains information on an Emergency Use Authorization of JYNNEOS (Smallpox and Monkeypox Vaccine, Live, Non-Replicating) for prevention of monkeypox disease in individuals determined to be at high risk for monkeypox infection.
Fact Sheet
Aug 9, 2022
This Fact Sheet contains information to help you understand the risks and benefits of receiving JYNNEOS, which you or your child may receive because there is an outbreak of mpox.
You are leaving Health.mil
The appearance of hyperlinks does not constitute endorsement by the Department of Defense of non-U.S. Government sites or the information, products, or services contained therein. Although the Defense Health Agency may or may not use these sites as additional distribution channels for Department of Defense information, it does not exercise editorial control over all of the information that you may find at these locations. Such links are provided consistent with the stated purpose of this website.
You are leaving Health.mil
View the external links disclaimer.
Last Updated: June 06, 2024